If you glance through the Security settings of your device, particularly an Android phone, you will also find the trusted credentials section. You may wonder as to what these are and the role they play in your device’s security.
Trusted credentials list the certificate authorities (CA) issuing security certificates for validating a server’s identity over secure connection. The source you need to access must have a certificate signed by a CA for your device to trust it. The trusted credentials can be system or user-based.
In this post, we’ll look at how to put trusted credentials on your Android device and how to check them.
What are trusted credentials on my phone?
Most websites and apps you attempt to access have an active certificate signed by a trustworthy certificate authority (CA) in the list for your device to trust.
A certificate is used to verify the identity of the site or app. Certificate authorities are organizations that issue secure certificates to verify the identity of a web or mail server.
Android’s Trusted Credentials is the trust store on your phone where these certificates are stored. It is used to check the certificate whenever you access a website, an app, or a mail server.
When your device tries to access a server, it comes across a certificate issued by a certificate authority. If the certificate is in your credentials store, your device will trust that certificate. If not, (untrusted CA), you will be warned to proceed with caution.
The trusted credentials settings are divided into two sections:
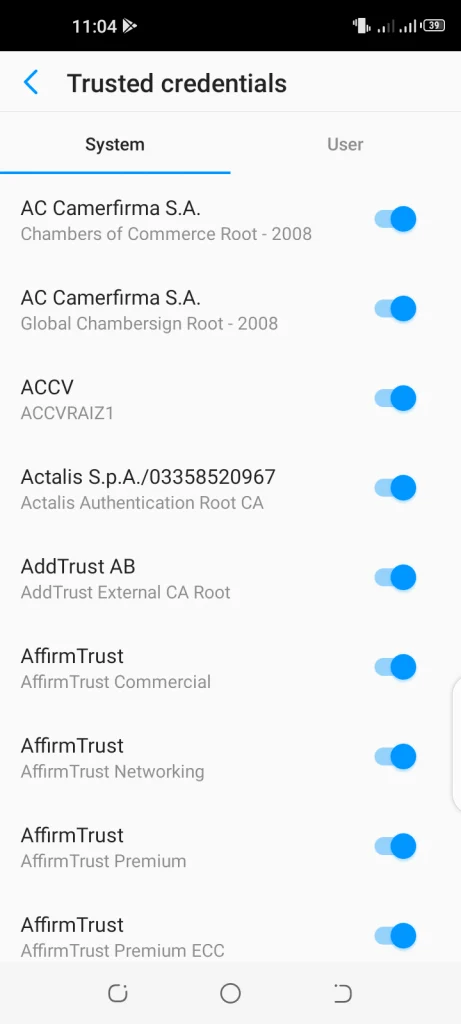
- The system section provides a list of trusted certificate authorities that come with your device.
- The user section lists all trusted certificate authorities that have been installed by you or an app. It may be blank if you didn’t install any CA certificate not already included with the device.
Do I need security certificates on my phone?
Trusted certificate authorities that issue security certificates are needed to keep the communications between your device and remote servers secure.
When you access a web or email server over a secure connection, your device checks that the website has a certificate issued by a trustworthy certificate authority. This confirms the authenticity of the server, helping make the access secure.
Having a validate certificate stored on your device also identifies your phone with the web server or app and grants your phone access to the website, app, or email account.
For example, when accessing your bank’s website, Trusted Credentials settings on your device ensure your banking information is sent to the right place.
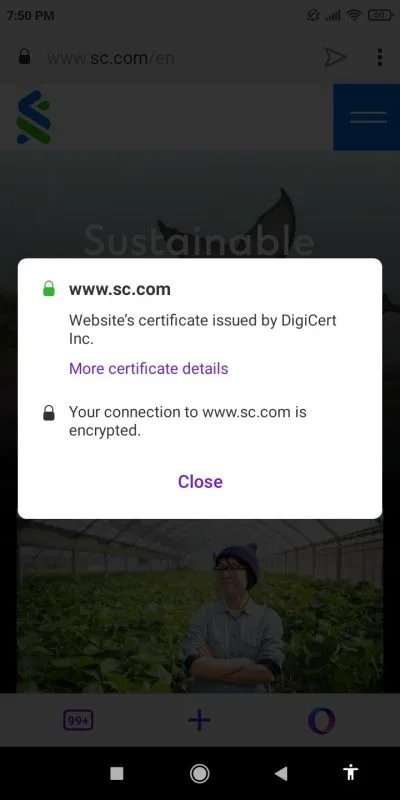
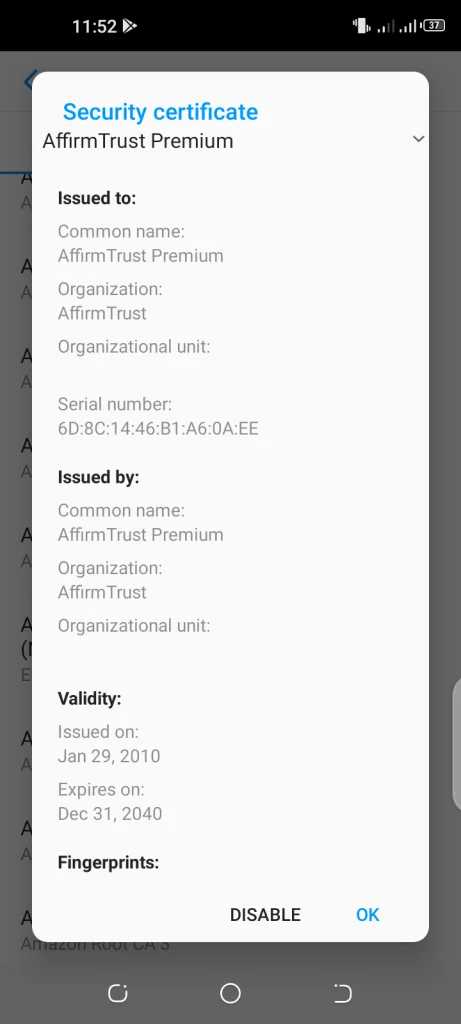
The security certificate indicates that a legitimate certificate authority has verified that the holder of the certificate (the bank site) is the actual owner of the bank’s domain.
You can check the certificate information by tapping on the lock icon on the left side of the address bar, then tapping Details.
How do I check trusted credentials on Android?
Depending on your Android phone and manufacturer, the procedure to check trusted credentials may be as follows:
- Open Settings app.
- Navigate to Security>Encryption & credentials>Trusted credentials. Note that some Android devices may have the setting named “View security Certificates” instead of “Trusted Credentials”.
- This will open the System tab. You can also tap on the user tab to view the trusted certificate authorities installed on your end.
- Tap on a certificate authority to view details such as validity and more. An option for disabling it is also provided.
Do I need the hundreds of trusted credentials on my phone?
Your phone needs these large amounts of trusted credentials because these are required for connection to secure sources from your Android device. These certificates are encrypted on your phone and used for VPN (Virtual Private Networks), exchange servers, Wi-Fi and ad-hoc networks, and more.
In other words, Android utilizes certificates for increased security and these certificates are needed to access secure networks or data.
What trusted credentials should I disable for an Android?
You should not disable trusted credentials in the system tab of an Android device as doing so may lead to the phone not recognizing and establishing secure connectivity to certificates issued by a specific CA.
It may also lead to security-related warnings on your device and you may no longer be able to visit certain websites as their certificates will have been removed from your device’s trusted credentials.
Generally speaking, you should not disable any credential unless there’s news that a CA has become untrustworthy.
You can disable security certificates listed in the user tab without any concern, as the apps installing these certificates will prompt you to install them again.
What happens if you clear credentials on Android?

If you clear the credentials on your Android device, all the security certificates that are installed will be removed.
As a result, your phone will not be able to recognize and establish a secure connection based on certificates issued by a specific CA.
This can lead to the Android OS and some apps with installed certificates not functioning properly. You may get warnings on your screen that a website isn’t trusted when you try to visit one.
As explained in the above section, you should generally avoid deleting credentials on your Android.
Should you delete expired certificates?
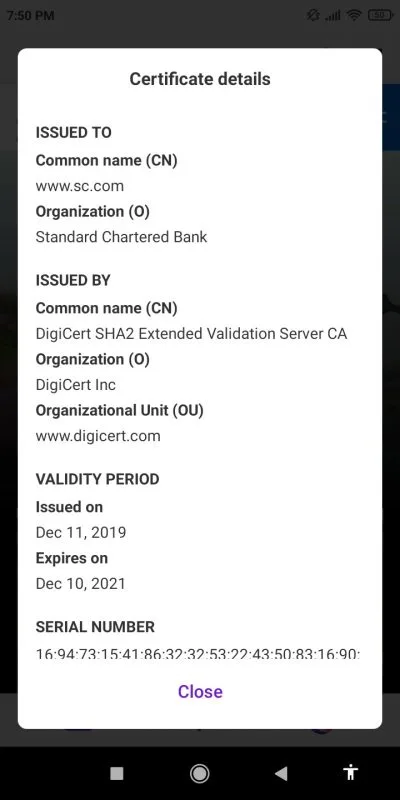
Expired certificates are no longer valid and you can delete them. An expired certificate will prevent your device to securely access a website or app that utilizes it. Android will mark out the expired certificate as invalid and there is no way its life can be extended.
When a certificate has expired, the certificate authority must issue a new certificate to replace the expired one, and it must be installed on your device. This is known as renewing the certificate.
You can view a certificate’s issue and expiry dates by tapping on a trusted credential as described above.
Where are certificates stored in Android?
The security certificates along with their keys are encrypted and stored in /data/misc/keystore. Since they are stored and managed by the Android system, they are encrypted and no-one can access or change them.
However, you can easily view the list of certificate authorities in the Settings app. You can also disable a certificate if required, as explained earlier.
How do I put credentials on my phone?
Once you have a security certificate downloaded or saved in your phone storage, you can install it on your Android device. In other words, you can put the credentials on the device through the following steps:
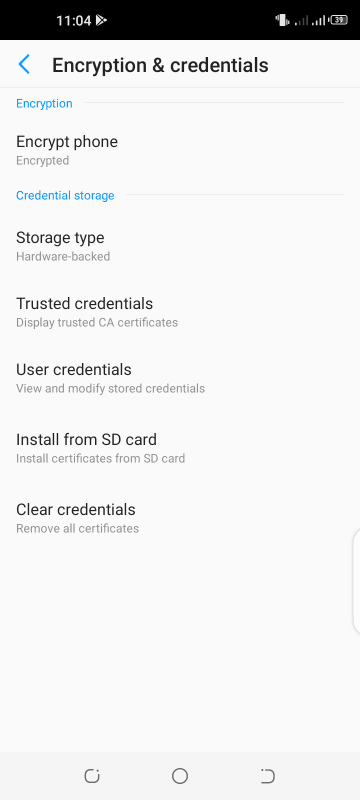
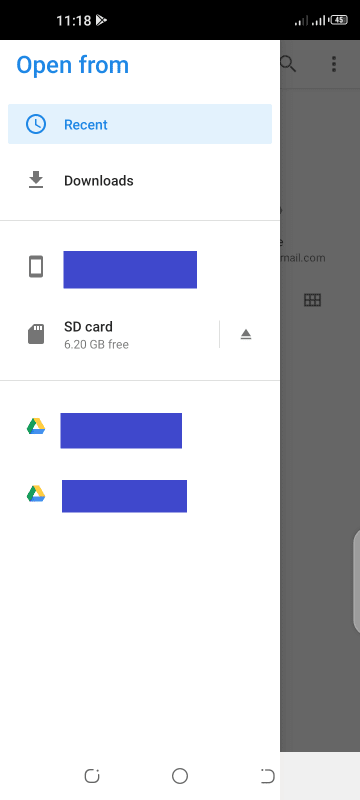
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Security > Encryption & credentials > Install from SD card.
- Tap on the three lines on the left and go to the location where the certificate is downloaded.
For instance, it could be the Downloads folder or a folder in your phone’s internal storage or microSD card. - Tap on the certificate file. You will then be asked to set up a Lock screen password, PIN, or pattern before installation. If you’ve already have one set up, you will be asked to enter it.
- Input a name for the certificate and choose how it will be used.
- Tap on OK.
How do I download certificates on Android?
You can download certificates on your Android device in any of the following ways:
Via a website
You can download certificates from websites of different companies such as certificate authorities in a browser on your Android phone. The files can be in different formats such as .cer and .crt and are usually saved to your device’s downloads folder.
Via email
You can also download a certificate through a link sent via email to your email address by a company such as a certificate authority or internet service provider.
You need to tap on the provided link usually to get the certificate on your device.
Through your system administrator
You can also acquire a security certificate through your organization’s system administrator.
How do I trust all certificates in Android?
The option to trust all certificates in Android is not present in the device’s Security settings. However, you can view system and user certificates issued by trusted certificate authority from your settings (see earlier).
You can certainly disable and enable individual system certificates that are required for your phone to work. As mentioned earlier, user certificates that you’ve installed can also be removed.
How do I trust a certificate on my iPhone?
As you know, a certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA) is also known as a root SSL certificate.
It’s necessary to turn on SSL trust for that certificate when you need to install a certificate profile that’s downloaded from a website or sent to you through email. This can be done on an iPhone in the following way:
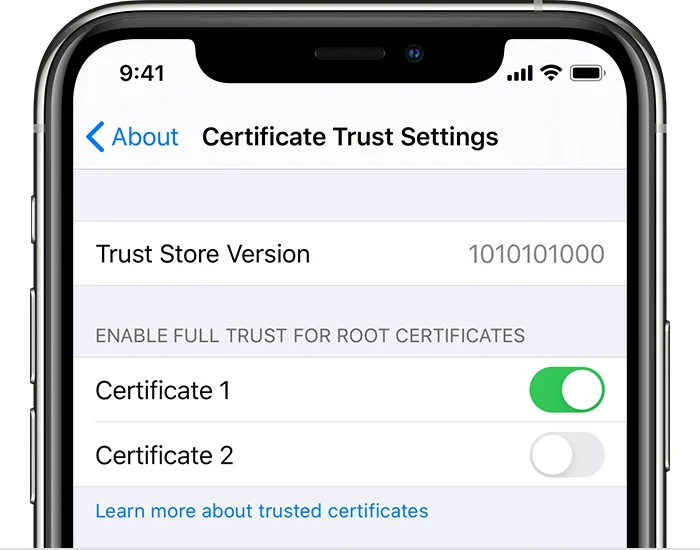
- Open Settings.
- Navigate to General > About > Certificate Trust Settings.
- Enable trust for the certificate by toggling its switch on; this can be found in the “Enable full trust for root certificates” section.
After this, the root SSL certificate will be trusted on your iPhone.
How do I fix security certificate error on Android?
A security certificate error is a common problem encountered by Android smartphone users, including with new and updated smartphones. There are a few ways that you can fix this issue.
1. Try to connect to a personal or private Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi connections are often insecure, so simply connecting to a private secured Wi-Fi network might resolve the issue.
2. Adjust your phone’s date and time
If the above doesn’t solve the issue, you can try fixing the date and time of your phone. Depending on your Android device, do the following:
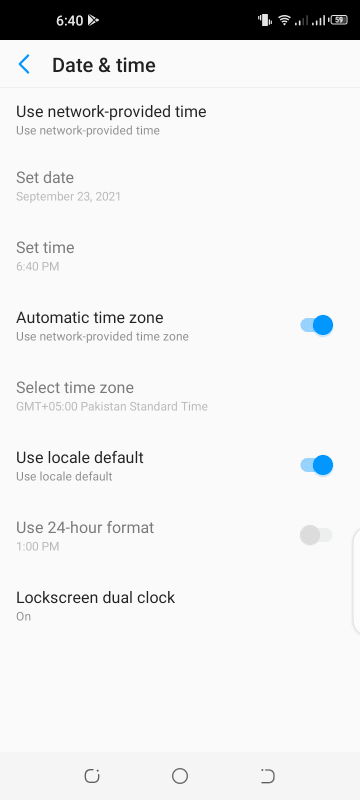
- Navigate to Settings > System > Date & Time, and toggle on the switch for automatic time zone.
- Also make sure to enable network-provided time.
3. Update your browser and clear browsing data
You can also try updating your browser (e.g. Chrome) to fix a security certificate error:
- Head over to the Google Play Store
- Search for the browser app (e.g. Chrome) and update it.
In some cases, clearing your browsing history might also fix the certificate error issue:
- Open Chrome and tap on the three dots on the right.
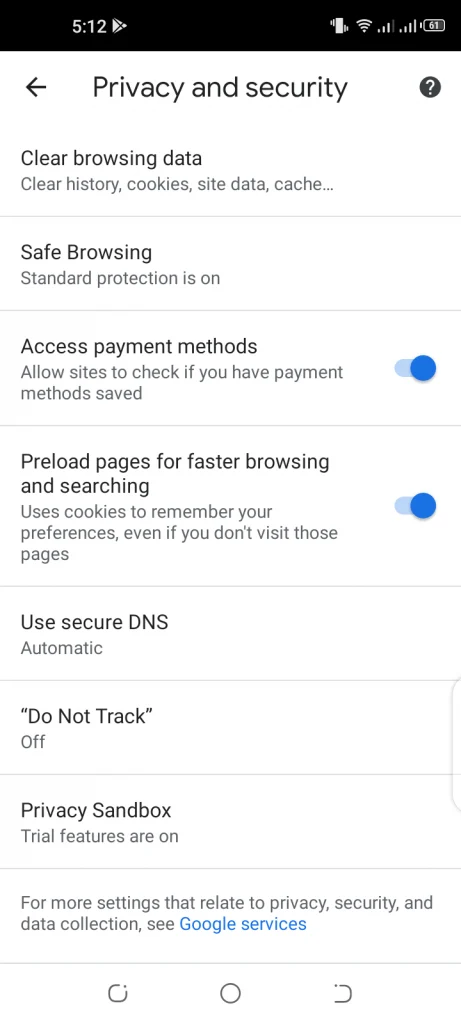
- Navigate to Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data.
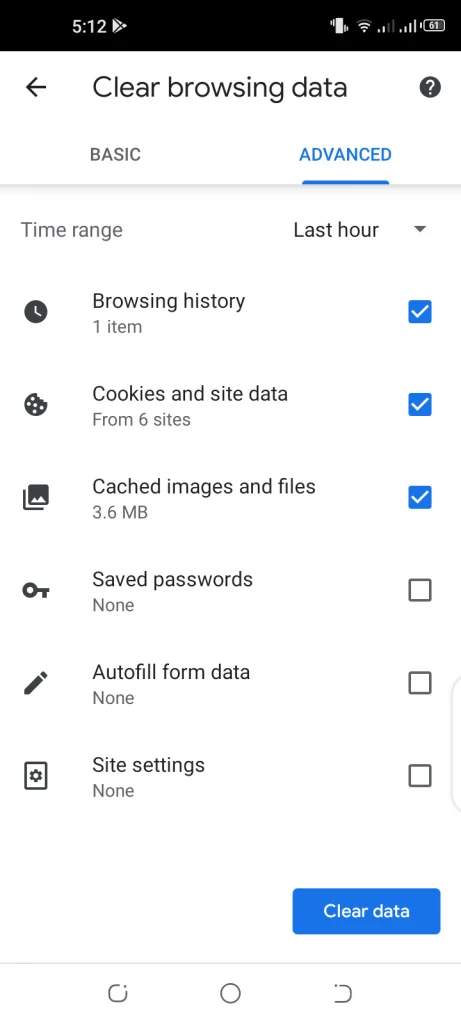
- Choose a time range on the next screen.
- Check the boxes including Browsing History, Cookies and Site data, and Cached Images and Files.
- Hit Clear Data.
Why does my phone say certificate not secure?
Sometimes, your Android device may tell you the certificate is not secure as you try to visit a website in a browser, or when you check your email. There can be multiple reasons for this:
- Incorrect date and time of your device
- Insecure internet connection such as Public Wi-Fi
- Browser is outdated
- Antivirus on your phone is blocking the website
- Problematic or insecure website
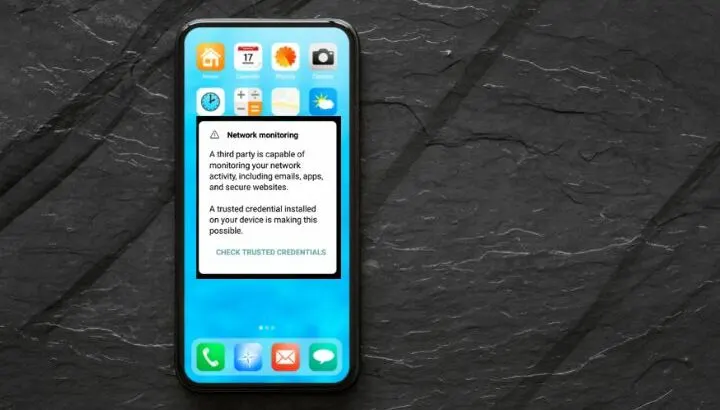
What does it mean when my phone says Network may be monitored?
You may get a notification on your Android phone that says the network may be monitored. Tapping on it results in a message that says a third party can monitor your network activity because of a trusted credential installed on your device.
The reason behind this message is that a security certificate has been installed on your phone manually by yourself or another user, or automatically through a website or third-party app.
This certificate is not issued by a pre-approved certificate authority that can be found in the system tab of Trusted Credentials.
The Android OS warns you about the possibility of a malicious certificate installed that can monitor your network, which could be harmful.
In some cases, however, the issue is due to a legitimate company (e.g. a hotspot provider) using self-issued certificates (instead of CA issued) on their hardware.
To fix this issue:
- Navigate to the user tab of Trusted Credentials.
- Tap on the installed security certificate and select Remove.
- Uninstall the third-party app that you installed before (if any).